
Simulating the planned surgical procedure, which resulted in inadequate ventilationĭespite adjustment of mechanical support.įig. 1 - Transverse computed tomography displaying left upper lobe pulmonaryĭue to the patient's hemodynamic lability, we attempted to insert a veno-venousĬannula into the jugular vein however, the vessel was too small to accept the Preoperatively, the patient was placed in the right lateral decubitus position, Management, we proceeded with left upper lobectomy to control the fistula. Due to repeated pneumothoraces with conservative Upper lobe with an associated bronchopleural fistula (BPF) ( Figure 1). Of the chest was consistent with pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE) of the left Ventilation (HFOV) to reduce peak and mean airway pressures. The patient was placed on high frequency oscillatory A secondĬhest tube was required the following day due to a recurrent left pneumothorax with Tension pneumothorax, which was treated by insertion of a pigtail catheter. Immediately after, the patient developed left-sided Postoperatively, the lung compliance improved: on POD 8, mediastinal and pleuralĬhest tubes were removed. Which was managed with an amiodarone drip with eventual addition of flecainide. Of SVT: at this time, suspicion arose of a concealed Wolff-Parkinson-White pathway, A few hours postoperatively, the patient again had episodes Lungs led to leaving the chest open, followed by delayed closure on the third Was relatively poor - necessitating high inspiratory pressures. After separation from bypass, the lung compliance
#Pulmonary barotrauma interventuons Patch#
Repair of his hypoplastic aortic arch by homograft patch enlargement and primaryĬlosure of his ASD – total cardiopulmonary bypass time was 153 minutes, andĬross-clamp time was 90 minutes. Last episode required acute administration of adenosine and prevention of subsequentĮpisodes was achieved with propranolol. Which was followed by recurrent episodes of SVT with a heart rate in the 300s the
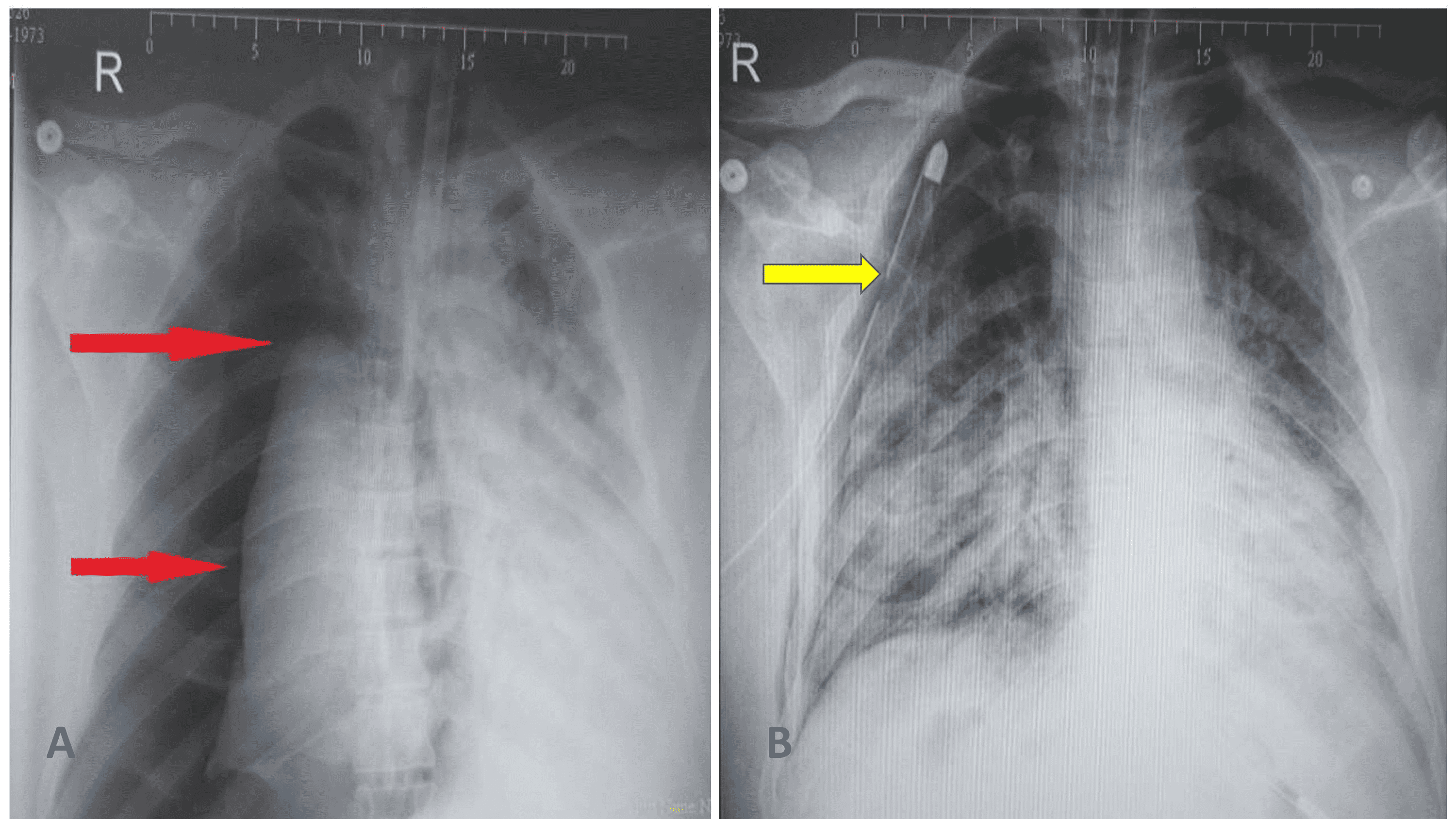
The next day, the patient developed ectopic atrial rhythm, Ventricle, and secundum atrial septal defect.

Postnatally, an electrocardiogramĭemonstrated periods of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and, an echocardiogramĬonfirmed the presence of a hypoplastic aortic arch, mildly hypoplastic left The fetus had episodes of narrow complex tachycardia with heart rate ranging fromġ80-305 bpm. Moderately dilated and hypertrophied right ventricle and a hypoplastic aortic arch. Prenatal history was notable for a fetal echocardiogram, which demonstrated The patient was born at 38 weeks of gestation via C-section delivery due to prolonged


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
